FRS IP Solution
The FRS IP Solution is an FPGA implementation (IP core) of High-availability Seamless Redundancy (HSR) and the Parallel Redundancy Protocol (PRP) integrated into an Ethernet Layer-2 switch. All the ports are triple-speed (10Mbps/100Mbps/1Gbps), and the internal wire-speed forwarding capability (gigabit Full-Duplex at all the ports at the same time) makes it one of the best-performing HSR/PRP switches in the market. Thanks to its scalability, the single IP core can be used in both low- and high-end FPGA-based devices. FRS has been validated using methods such as hardware-accelerated simulation to guarantee the quality of the IP. HSR is widely used in substation automation (smart grid), but use cases also include industrial automation and transportation.
Features
- Configurable as a 3- to 8-port layer 2 Ethernet switch
- All ports are triple-speed (10 Mbit/s / 100 Mbit/s / 1 Gbit/s)
- Internal wire-speed forwarding capability (Gigabit full-duplex at all the ports at the same time)
- Compatible with IEC 62439-3 Clause 5 “High-availability Seamless Redundancy (HSR)” (version 4.0)
- Compatible with IEC 62439-3 Clause 4 ”Parallel Redundancy Protocol (PRP)”
- Integral PTP support for applications where time synchronization is needed by using IEEE1588-2008 Precision Time Protocol v2 (PTP)
- IEEE1588v2 End-to-end one-step Transparent Clock Functionality
- IEEE1588v2 Peer-to-peer Transparent Clock support functions\
- More PTP functions can be added with the XR7 PTP software stack, which is compatible with the FRS IP Solution
- Achieves nanosecond-class accuracy in clock transfer when using Gigabit fiber Ethernet
- Ethernet packet forwarding at wire-speed, non-blocking
- All of the ports of FRS can be either copper or fiber Ethernet interfaces, or connected to other FPGA blocks
- Ethernet packet filter and prioritization on each of the ports
- Cut-through and store-and-forward operation
- HSR RedBox, HSR End-node, HSR QuadBox, PRP RedBox, and DANP support
- Compatible with IEEE standard 802.1D Media Access Control (MAC) bridges
- Interface options – MII and GMII, interface adapters available for RMII, RGMII, EMAC, and Triple Mode (SGMII, 100BASE-FX, and 1000BASE-X)
- Register interface for accessing control and status registers
XR7 Redundancy Supervision
XR7 Redundancy Supervision is an additional software stack used with the FRS IP Solution. It provides the HSR/PRP supervision feature described in IEC62439-3 standard (HSR/PRP), which monitors HSR/PRP redundancy operation. If there is a single failure (e.g., link break) in the HSR or PRP network, it cannot be detected by any other protocol or application. That is why it is critical to have HSR/PRP supervision running in a redundant network. XR7 Redundancy Supervision provides this network monitoring information.
XR7 Redundancy Supervision does not include a network management system; therefore, the information it provides should be delivered to the network user, for example, by utilizing your own network management or monitoring system.
The software is written in C and is provided as source code. It is available for Linux but is also easily portable to other operating systems. Porting requires changes to be made only to the system-specific interfaces. This allows the common software module, containing the core functionality, to remain unchanged.
Technologies
High-availability Seamless Redundancy (HSR) is a standard (IEC 62439-3 Clause 5) fulfilling the need for reliable Ethernet. It is suitable for applications that require short reaction times and high availability. With HSR, a network can be made very robust with zero reaction time in case of a single failure, with predictable latency and with less cost than with other Ethernet redundancy solutions.
Many critical applications require a network with zero downtime. The network is fully operational even during maintenance, as any device can be disconnected and replaced without breaking the network connectivity. This makes the network very reliable and highly available.
Find out more on our technology page.
The Parallel Redundancy Protocol (PRP) is an IEC standard (IEC 62439-3 Clause 4) providing redundant Ethernet. Under PRP, each node is connected to two separate parallel LANs, parallel Local Area Networks (LANs). Source nodes send two copies of each packet, one over each network. When a destination node receives a packet, it accepts the first copy and discards the second copy, eliminating the duplicate.
HSR is more cost-effective than PRP because HSR requires significantly less cabling. Therefore, HSR can be considered the most effective redundancy solution available for Ethernet at the moment.
Find out more on our technology page.
Configuration
FRS is highly configurable. For example, a 4-port FRS can be used to implement End Nodes and RedBoxes. Typically one of the Ethernet interfaces is internal, for the device internal CPU to be able to access the network. Two external Ethernet interfaces connect to the HSR ring and the fourth interface is an interlink port. At least a 4-port FRS is recommended, as then no separate RedBoxes are needed and the devices can be connected straight to the FRS.
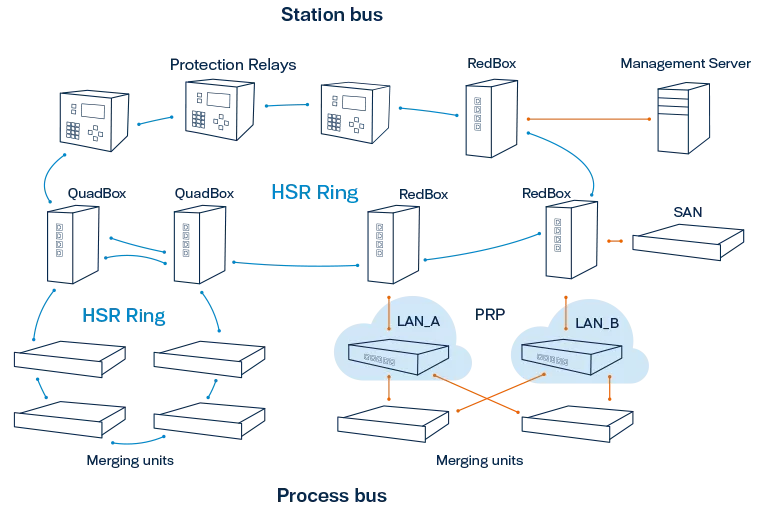
Example of a redundant network using HSR
